A patient’s story
When Sarah first came to the clinic, she was exhausted from months of bloating, unpredictable bowel habits, and a constant feeling of “something not being right” with her digestion. She had been told it might be IBS, then perhaps SIBO, and another practitioner mentioned dysbiosis. “Aren’t they all the same thing?” she asked, understandably confused.
This is a question we hear often – and one worth answering properly. While SIBO and dysbiosis both involve bacteria in the gut, they describe different problems occurring in different parts of the digestive system. Understanding the distinction helps guide the right investigations, treatment, and expectations for recovery.
What is SIBO?
Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) occurs when bacteria that normally reside in the large intestine begin to multiply excessively in the small intestine, where bacterial numbers are usually low.
This shift in location disrupts digestion and nutrient absorption. The overgrowth leads to fermentation of carbohydrates, producing excess hydrogen or methane gas – the key culprits behind bloating, discomfort, and altered bowel habits.
Common symptoms include:
Bloating that worsens through the day
Excessive gas or belching
Abdominal pain or distension
Diarrhoea, constipation, or alternating patterns
Fatigue, brain fog, and nutrient deficiencies (especially B12, iron, and fat-soluble vitamins)
Typical causes include:
Impaired gut motility, such as after infections or due to diabetes, hypothyroidism, or connective tissue disorders
Long-term use of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs), which lower stomach acid – a natural barrier against bacterial migration
Previous abdominal surgery leading to adhesions or altered anatomy
Underlying IBS or inflammatory bowel conditions
At LSDC in Central London, patients with suspected SIBO often undergo a hydrogen-methane breath test, the standard non-invasive method for diagnosis. The test measures gas production after ingesting a sugar substrate (usually lactulose or glucose). A characteristic early rise in gas indicates bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine.
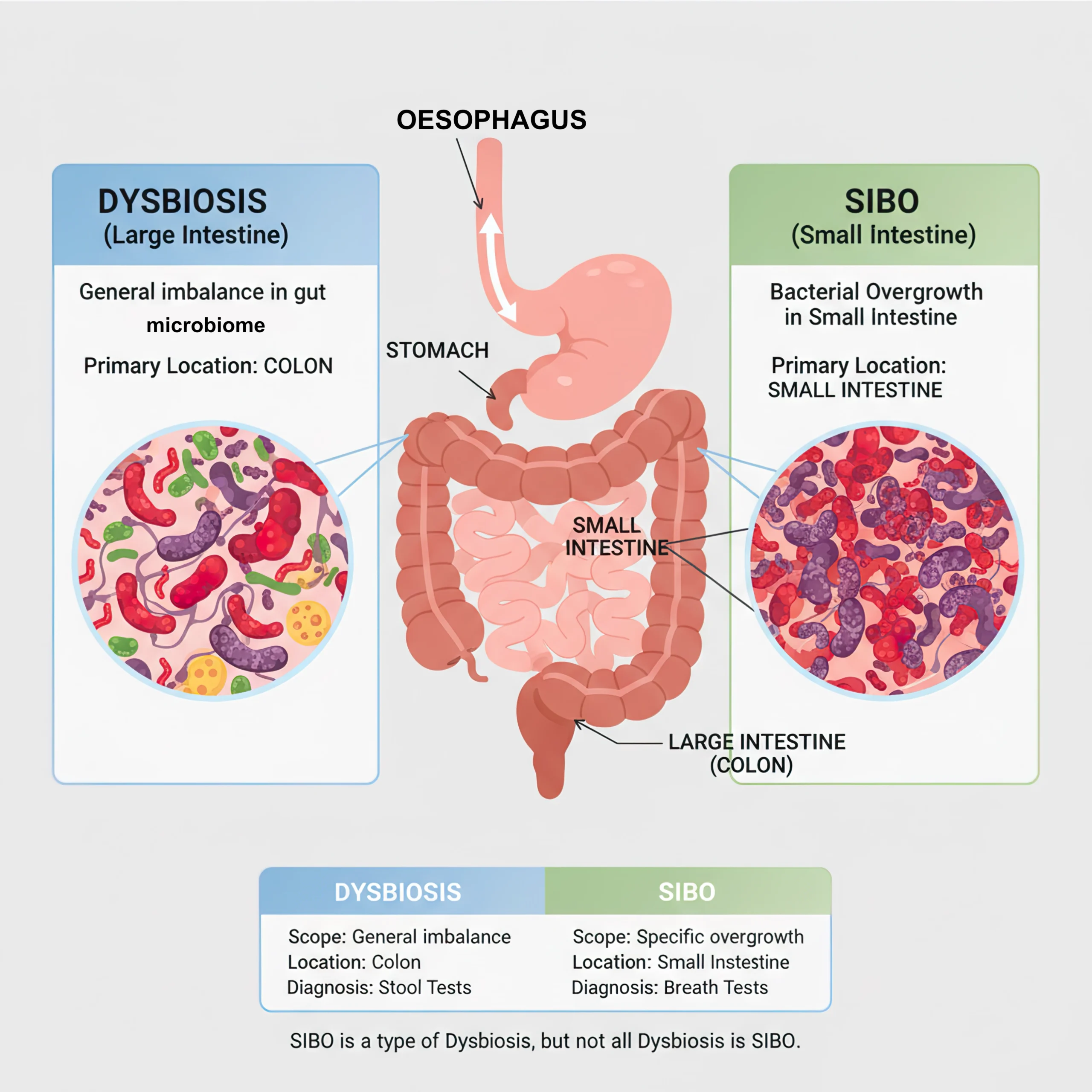
What is Dysbiosis?
Dysbiosis refers to an imbalance in the gut microbiota: the community of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that live throughout the digestive tract.
Unlike SIBO, which is about bacteria in the wrong place, dysbiosis is about the wrong mix of microbes: too many harmful species, too few beneficial ones, or reduced diversity overall.
Common symptoms can include:
Bloating or discomfort
Irregular bowel habits (diarrhoea, constipation, or both)
Food sensitivities or intolerances
Low energy and reduced concentration
Skin issues, such as acne or eczema
Worsening mood or anxiety (due to the gut–brain connection)
Causes of dysbiosis may include:
Repeated or long-term antibiotic use
Highly processed diets lacking fibre and plant variety
Chronic stress and poor sleep
Frequent infections or immune dysfunction
Overuse of antiseptic mouthwash or PPI medication
Underlying digestive disorders, such as IBD or coeliac disease
At LSDC, when dysbiosis is suspected, a comprehensive stool microbiome test can be arranged to analyse microbial composition, digestive enzyme activity, and markers of inflammation. These insights guide tailored interventions, including targeted probiotics, dietary therapy, and gut-healing strategies.
SIBO and Dysbiosis: How They Intersect
SIBO and dysbiosis are not mutually exclusive. In fact, SIBO is a specific form of dysbiosis: but one that’s localised to the small intestine.
When bacteria colonise where they shouldn’t, they can alter the entire ecosystem of the gut. Similarly, a pre-existing imbalance (dysbiosis) can create conditions that allow SIBO to develop.
For instance:
Dysbiosis in the colon can disrupt motility and fermentation patterns, promoting reflux of bacteria into the small intestine.
SIBO itself can worsen dysbiosis by changing nutrient availability and competing with beneficial microbes.
The key distinction is location and mechanism:
SIBO = overgrowth in the small intestine
Dysbiosis = imbalance anywhere in the gut
Comparing SIBO and Dysbiosis
Feature | SIBO | Dysbiosis |
|---|---|---|
Location | Small intestine | Any part of the gut (small or large intestine) |
Definition | Overgrowth of bacteria where few should exist | Imbalance in overall gut microbiota composition |
Primary mechanism | Migration and overgrowth of colonic-type bacteria in the small bowel | Loss of beneficial species and/or excess of pathogenic microbes |
Main symptoms | Bloating, gas, abdominal discomfort, diarrhoea or constipation, nutrient malabsorption | Variable: bloating, irregular bowels, fatigue, skin or mood changes |
Diagnostic tests | Hydrogen/methane breath test | Stool microbiome analysis, clinical assessment |
Common causes | Impaired motility, chronic PPI use, structural changes, IBS, diabetes | Antibiotics, poor diet, stress, infections, low fibre intake |
Treatment approach | Targeted antibiotics (e.g. rifaximin ± neomycin), prokinetics, low FODMAP or elemental diet | Probiotics, prebiotics, diet diversification, microbial rebalancing |
Relation to each other | A type of dysbiosis limited to the small intestine | A broader imbalance that may predispose to or result from SIBO |
How They Are Treated Differently
While both conditions affect the gut microbiome, the approach to treatment differs significantly. For SIBO, the goal is to reduce bacterial load in the small intestine and restore normal motility.
Treatment usually includes:
Antibiotics such as rifaximin (and sometimes neomycin for methane-predominant SIBO)
Herbal antimicrobials, e.g. oregano oil or berberine, for mild or recurrent cases
Dietary therapy, often a structured low FODMAP plan or temporary elemental diet
Prokinetic medication after treatment to prevent recurrence
For dysbiosis, the focus is on rebalancing the gut ecosystem rather than clearing bacteria.
This may involve:
High-fibre, plant-rich diets to promote microbial diversity
Specific probiotics or prebiotics guided by microbiome testing
Stress reduction, exercise, and adequate sleep
Limiting antibiotics or acid-suppressing drugs where possible
Both conditions benefit from a personalised, stepwise approach, especially when symptoms overlap
When to Seek Help
If you experience persistent bloating, unpredictable bowel habits, or discomfort that doesn’t respond to basic dietary changes, it’s important not to self-diagnose.
At LSDC Clinic in Central London, we take a comprehensive, evidence-based approach to gut healt: from advanced breath testing for SIBO to gut microbiome analysis for dysbiosis. Each plan is individually tailored to uncover the root cause rather than just managing symptoms.
Treatment for SIBO and Dysbiosis
Treating SIBO focuses on reducing bacterial overgrowth and improving gut movement. This may involve short courses of rifaximin-based antibiotics or herbal antimicrobials, supported by gentle dietary adjustments and motility aids to prevent recurrence.
Managing Dysbiosis, on the other hand, aims to restore microbial balance through a high-fibre, varied diet, probiotics, and lifestyle measures such as stress management and limiting unnecessary antibiotics.
At LSDC, we take a targeted approach, using advanced breath testing and microbiome analysis to pinpoint whether the imbalance is due to SIBO, broader dysbiosis, or both, allowing for treatment that’s precise, evidence-based, and truly personal.
