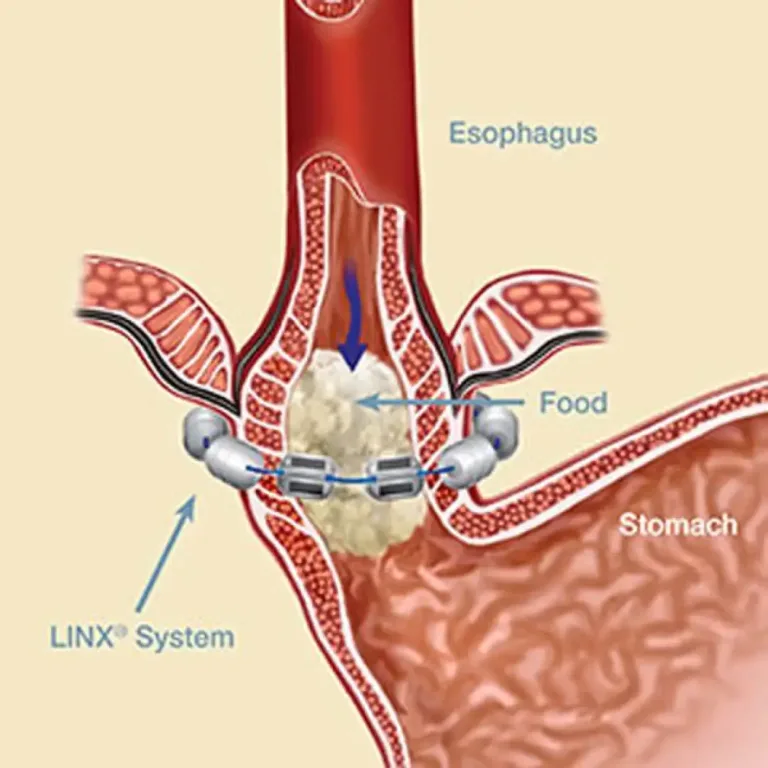
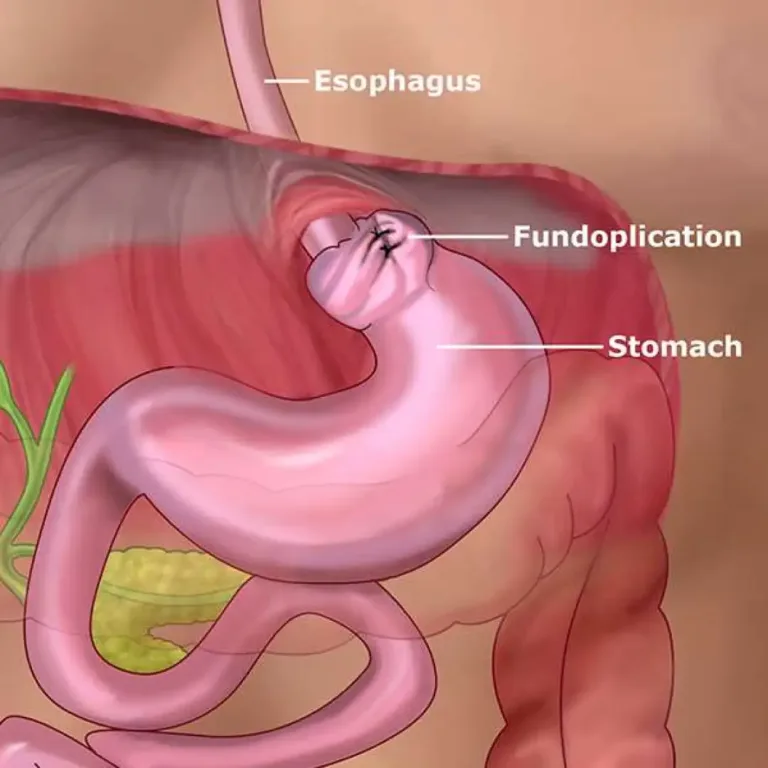
This article provides guidance on bloating symptoms, including how to identify its causes and how to begin addressing digestive issues. If you are experiencing bloating, we recommend consulting with one of our gastroenterologists to receive expert care and advice.
Related Symptoms
- Abdominal pain
- Acid reflux (heartburn) and indigestion
- Belching and burping
- Diarrhoea
What is bloating?
Abdominal bloating, medically known as abdominal distension, is a condition that causes swelling or a feeling of fullness in the belly. Common symptoms of bloating include discomfort such as abdominal pain, excessive wind, burping or flatulence, and the urgent need to have a bowel movement. This is a prevalent health issue that can be caused by several factors, such as a build-up of gas in the lower digestive tract or fluid retention. Our team of specialists can assist in identifying the underlying cause of your bloating symptoms. Please book an appointment with one of our gastroenterologists for further evaluation and treatment.
Symptoms
- Belching and burping
- Constipation
- Diarrhoea
- Fever
- Heartburn (acid reflux)
- Indigestion (dyspepsia)
- Nausea and vomiting
These symptoms may be caused by a gastrointestinal infection. We recommend reviewing any medications you are currently taking as certain drugs, such as ibuprofen, can result in stomach irritation and bloating as side effects.
Typically, gas and bloating are regarded as more of an annoyance than a cause for concern. Bloating symptoms are not always accompanied by abdominal pain, and there are typically no reasons for alarm.
Causes
- What or how you eat
- Your physical fitness
- Your age
- Hormone changes (especially during the menstrual cycle and pregnancy)
- Lifestyle factors such as stress, anxiety or depression.
Bloating symptoms often emerge after eating a big meal, especially if you’ve eaten nothing for a few hours. In some cases, though, bloating is a symptom of a chronic disease or condition.
Other common bloating symptom triggers include:
- Spicy foods
- Dairy products
- Gluten
- Foods that are high in carbohydrates, salt or fat
- Alcohol
- Caffeine
- Fizzy carbonated drinks
Maintain a food diary over several weeks to keep track of specific items that may trigger a sensitivity in your body. Eliminate these items from your diet one by one, making it easier to identify potential causes. Our specialists can assist in identifying the probable triggers in your diet.
Diagnosis
It is crucial to be mindful that there may be significant underlying factors that can impact your digestive system. These include:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Coeliac disease
- Diabetes
- Inflammatory bowel disease/ Crohn’s disease
- Small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)
- Endometriosis
- Diverticular disease and diverticulitis
- Cancer
- Liver disease
If you encounter one or more of the subsequent symptoms, it is recommended that you consult with one of our specialists to receive an accurate diagnosis.
- Persistent pain and/or swelling
- Blood in your bowel movements (stools will appear very dark)
- Vaginal bleeding when you’re not having your period
- Frequent, severe vomiting
- A high fever
- Unexpected weight loss.
To rule out any serious conditions you may need tests and scans. These can involve:
- X-ray, sometimes involving a barium swallow test
- Abdominal scans such as a CT or MRI
- Blood tests and stool tests to check for infections, allergies such as lactose intolerance or diseases
Diagnostic procedures such as imaging or biopsy can be performed using a thin and flexible instrument known as an endoscope. A gastroscopy is used when the instrument is passed through the mouth, while a colonoscopy is used when it is passed through the rectum. Our specialists may recommend these procedures to diagnose the cause of your digestive symptoms.
Treatments
Determining the underlying cause of bloating symptoms can be a challenging task. If you are experiencing persistent bloating, begin by assessing your diet. Consider if you are drinking sufficient water, eating too quickly, or chewing gum, which can cause you to swallow air.
We suggest consuming smaller portions of food and eating slowly. Avoid consuming unhealthy food and restrict the intake of gas-producing ingredients, such as beans and cabbage.
Following a diagnostic test, our specialists can recommend the most appropriate treatment for any specific conditions detected.