Achalasia
Conditions
Achalasia
Achalasia is a rare condition of the esophagus, the tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. It occurs when the muscle at the bottom of the esophagus (the lower esophageal sphincter) fails to relax properly, making it difficult for food and liquid to pass into the stomach.
Symptoms of achalasia can include difficulty swallowing, regurgitation of food, chest pain, and weight loss. The exact cause of achalasia is not known, but it is believed to be related to a problem with the nerve supply to the lower esophageal sphincter.
Diagnosis of achalasia may involve a series of tests, including X-rays, a barium swallow test, and an esophageal manometry test to measure the pressure in the lower esophageal sphincter.
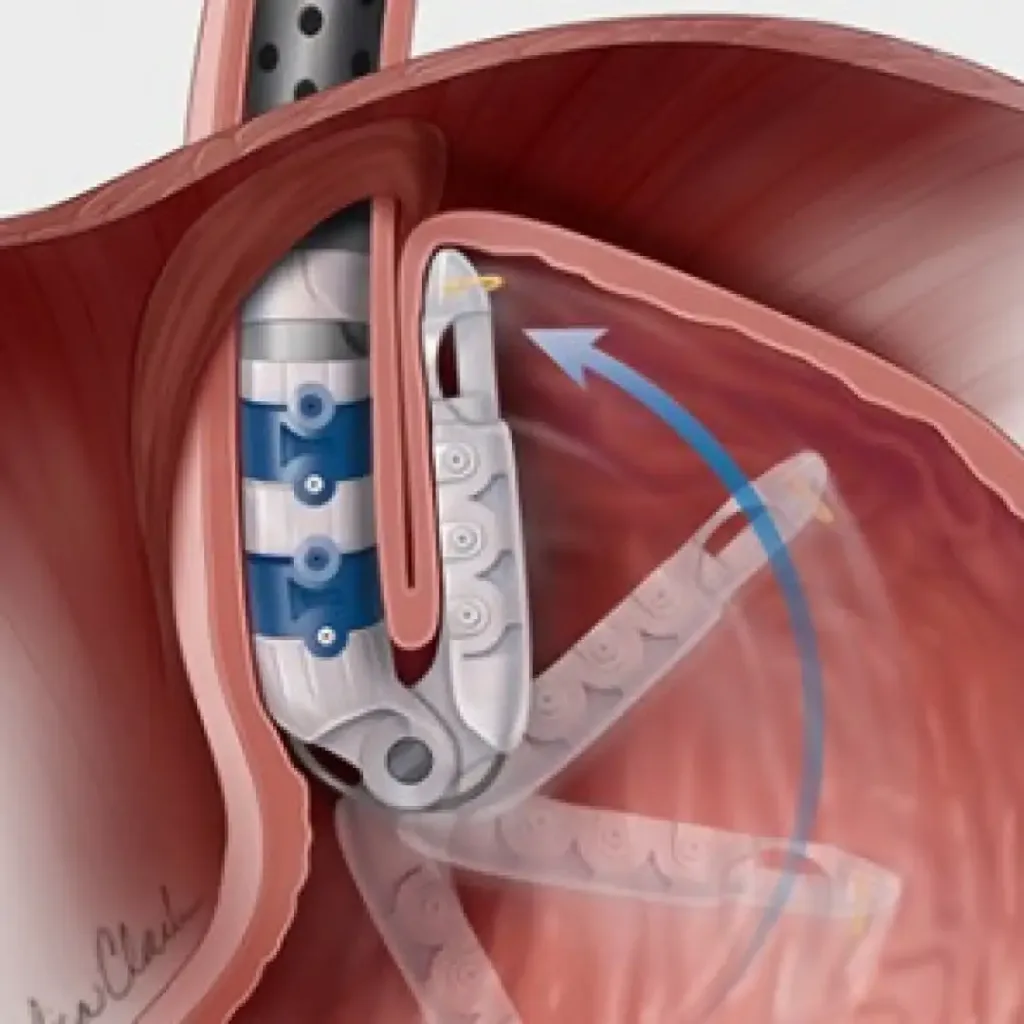
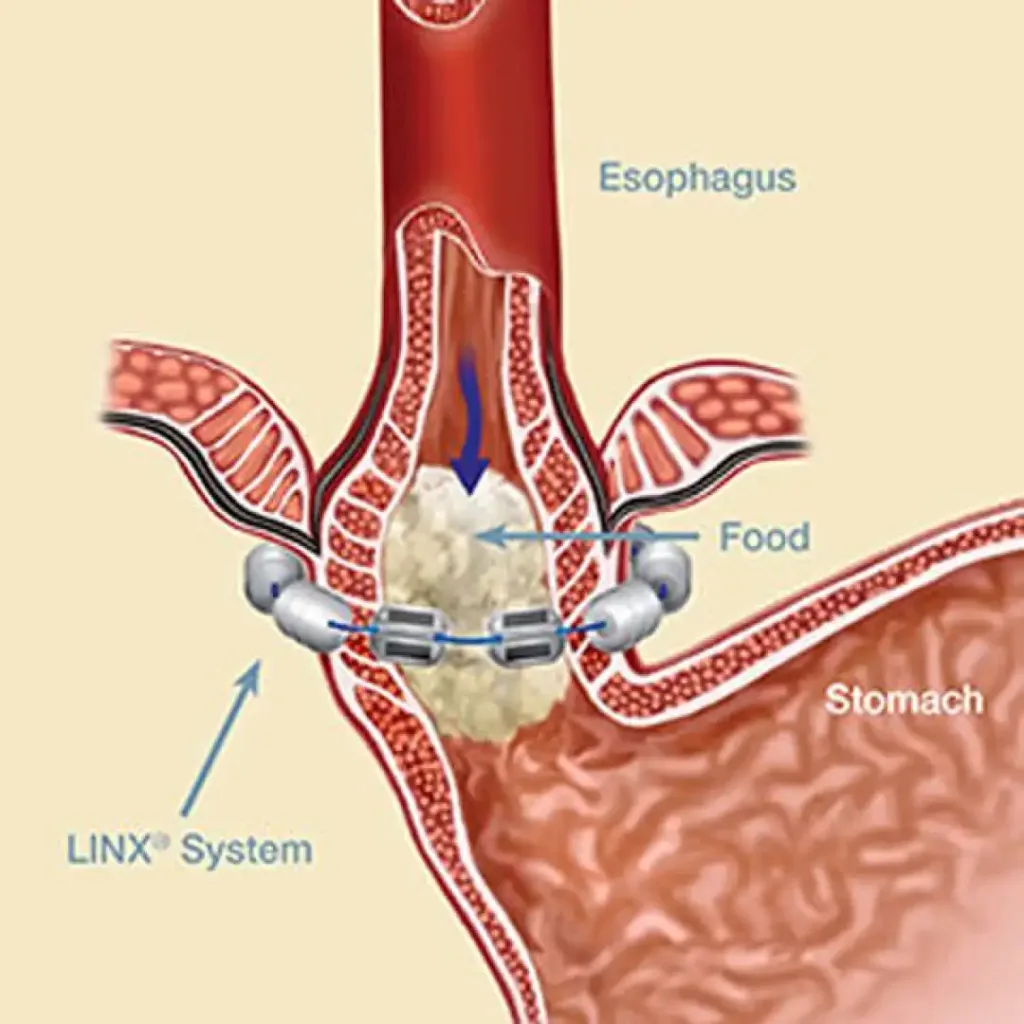
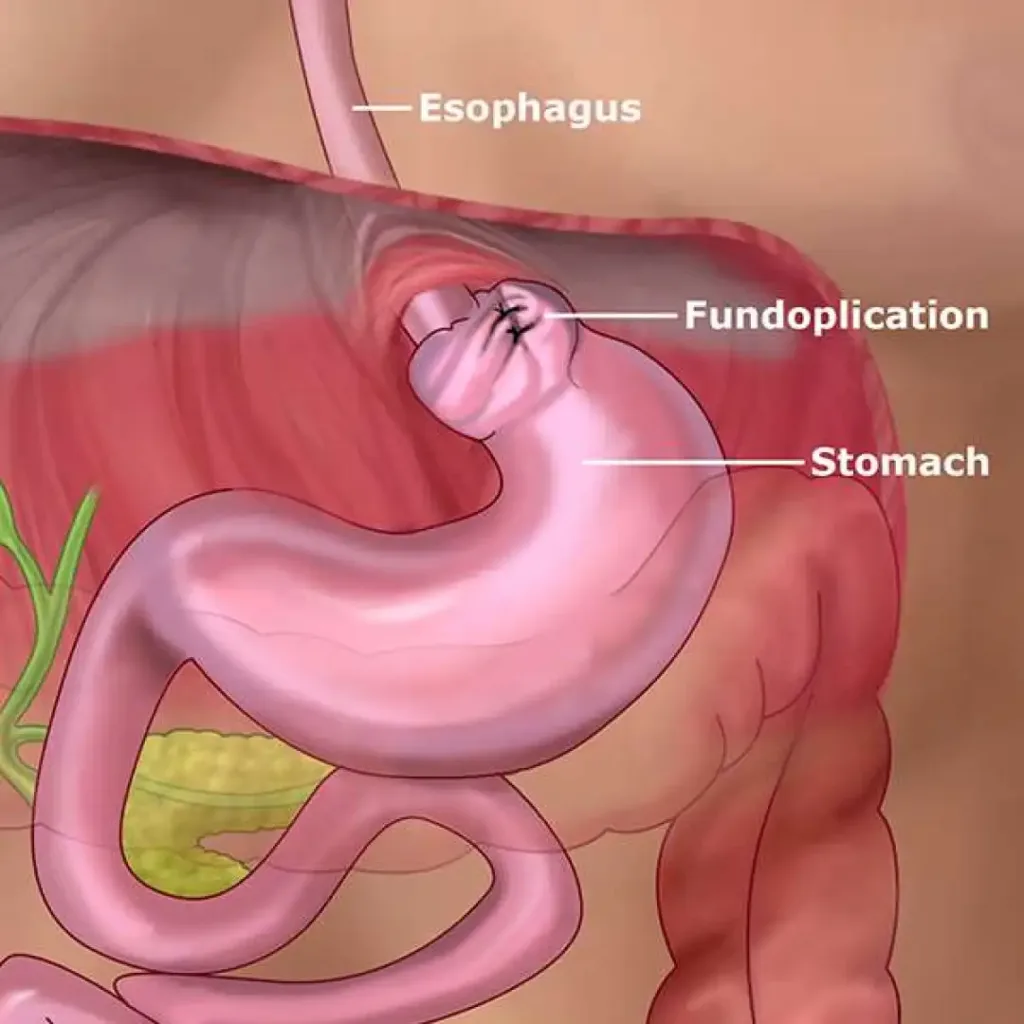
Treatment for achalasia typically involves procedures to relax the lower esophageal sphincter and improve the passage of food into the stomach. This can include medications, dilation of the esophagus with a balloon, or surgical procedures to cut the muscle at the bottom of the esophagus. In some cases, dietary modifications and lifestyle changes may also be recommended to manage symptoms.