What is a transnasal gastroscopy ?
Gastroenterology
What is a transnasal gastroscopy ?
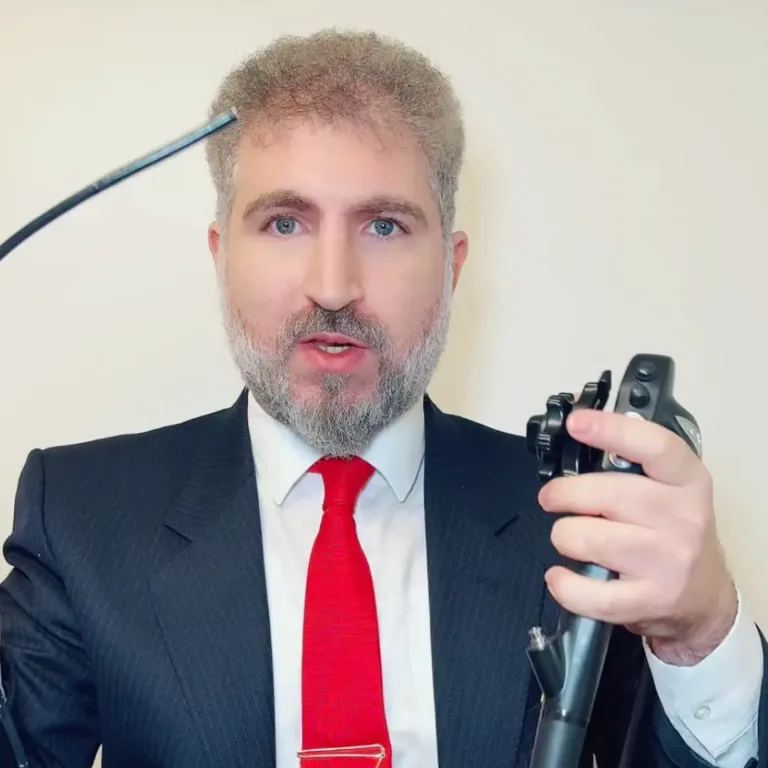
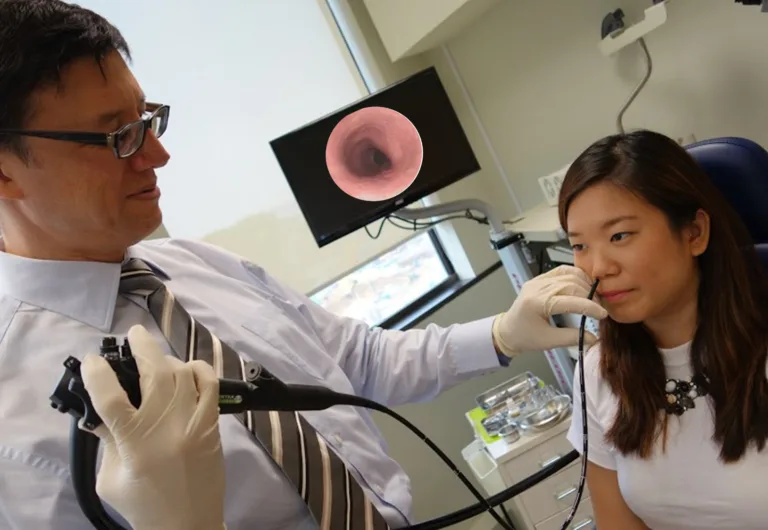
Medical advancements continue to redefine the landscape of diagnostic procedures, and one such innovation gaining prominence is the transnasal gastroscopy. Unlike traditional methods, this minimally invasive approach offers patients a more comfortable and convenient experience when examining the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Understanding Transnasal Gastroscopy:
Transnasal gastroscopy, also known as transnasal esophagoscopy or transnasal endoscopy, involves the insertion of a thin, flexible endoscope through the nasal passages to visualize the upper digestive system. Unlike conventional gastroscopy, which enters through the mouth, this procedure eliminates the need for sedation and offers a more patient-friendly alternative.
Benefits of Transnasal Gastroscopy:
Reduced Discomfort: The transnasal approach minimizes discomfort associated with traditional gastroscopy, as it bypasses the throat and avoids triggering the gag reflex.
No Sedation Required: Patients undergoing transnasal gastroscopy often appreciate the absence of sedation, allowing them to resume their daily activities promptly after the procedure.
Convenience and Accessibility: The procedure is generally quicker and can be performed in an outpatient setting, providing a convenient option for individuals with busy schedules.
Enhanced Tolerance: The gentle and flexible nature of the transnasal endoscope enhances patient tolerance, making it particularly suitable for those who may be hesitant about traditional gastroscopy.
Considerations and Preparation:
While transnasal gastroscopy offers numerous advantages, it may not be suitable for everyone. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate diagnostic approach based on their individual needs and medical history.
Conclusion:
The evolution of medical technology continues to bring about procedures that prioritize patient comfort without compromising diagnostic accuracy. Transnasal gastroscopy represents a step forward in this direction, offering a less invasive and more convenient option for examining the upper gastrointestinal tract. As healthcare advances, embracing such innovations ensures that patients can undergo necessary diagnostic procedures with increased ease and confidence.
Schedule an appointment
Related Articles
What is a transnasal gastroscopy ? Read More »